Amazon DynamoDBは高速&拡張可能なNoSQLのDBです
この記事は公開されてから1年以上経過しています。情報が古い可能性がありますので、ご注意ください。
Amazon DynamoDBとは?
Amazon DynamoDBは、シームレスに拡張ができ、高速で予測可能なパフォーマンスを提供する、フルマネージドのNoSQL(非RDBMS)です。これは、データベース管理、パフォーマンス、スケーラビリティ、および信頼性のコアな問題に対処するために設計されています。Amazon DynamoDBは、お客様が少額の料金を支払うことによって、高可用性データベースのスケーリングとオペレーションの管理負担を軽減します。
Amazon DynamoDBのサービス特徴
Amazon DynamoDB
- スケーラブル
- スループット供給
- 自動ストレージ拡張
- 完全に分散された非共有アーキテクチャー
- 高速で予測可能なパフォーマンス
- 容易な管理
- フォールトトレラント済み
- フレキシブル
- 強い一貫性、原子性
- 費用対効果のある
- セキュア
- モニタリング
- EMR(Elastic Map Reduce)連携
Amazon DynamoDBのデータモデルについて
主な要素は、テーブル(Table)、アイテム(Item)、属性(Attribute)です。アイテム例を以下に示します。
{
Id = 101
ProductName = "Book 101 Title"
ISBN = "111-1111111111"
Authors = [ "Author 1", "Author 2" ]
Price = -2
Dimensions = "8.5 x 11.0 x 0.5"
PageCount = 500
InPublication = 1
ProductCategory = "Book"
}
テーブルを作成する際、プライマリキーを設定することができます。データタイプは以下の2種類です。
- スカラ型:NumberとString
- 複合型:Number集合とString集合
サポートされている操作について
Amazon DynamoDBでサポートされている操作は以下です。
- テーブル操作
- アイテム操作
- クエリーとスキャン
- 一貫性のある読み取り:結果整合性と読み取り一貫性を選べます
- 条件付き更新と並行処理
供給されるスループットについて
テーブルを作成や更新するとき、スループットを指定することができます。基本的な考え方は、1秒間にいくつの書き込みと読み込みをする必要があるか単位で指定します。
- 書き込み単位:1秒間に1KBの1アイテムを一貫性書き込み、結果整合性の場合には2アイテム
- 読み込み単位:1秒間に1KBの1アイテムを読み取り
例えば、一貫性のある書き込みで、512Byteのアイテムを1秒間に100件行いたい場合、100単位の供給を必要とします。例えば、読み取りで、1.5KBのアイテムを1秒間に100件行いたい場合には、200単位の共有を必要とします。もし、500単位の供給を利用する場合、1KBのアイテム問い合わせを1秒間に500件取得するのと、1KBのアイテム10件を1秒間に50回取得するのは同じ計算です。
REST APIでアクセスする
Amazon DynamoDBに対してREST APIを使ってアクセスする際のエンドポイントは以下になります。
- http://dynamodb.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
- https://dynamodb.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
サンプルから学んでみよう
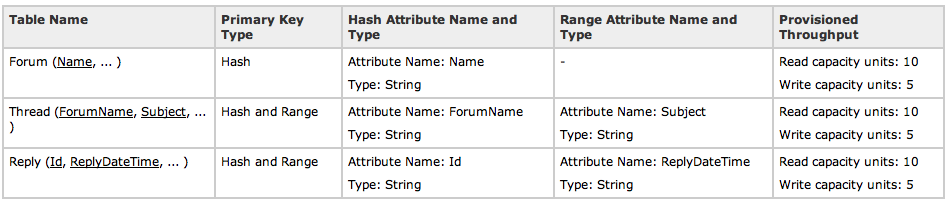
ユースケース1:商品カタログのデータベース
商品ごとに属性情報が異なるカタログのテーブルを作ってみます。
ユースケース2:フォーラムアプリ
ユーザーがスレッドを立ててコミュニケーションをするフォーラムを作ってみます。
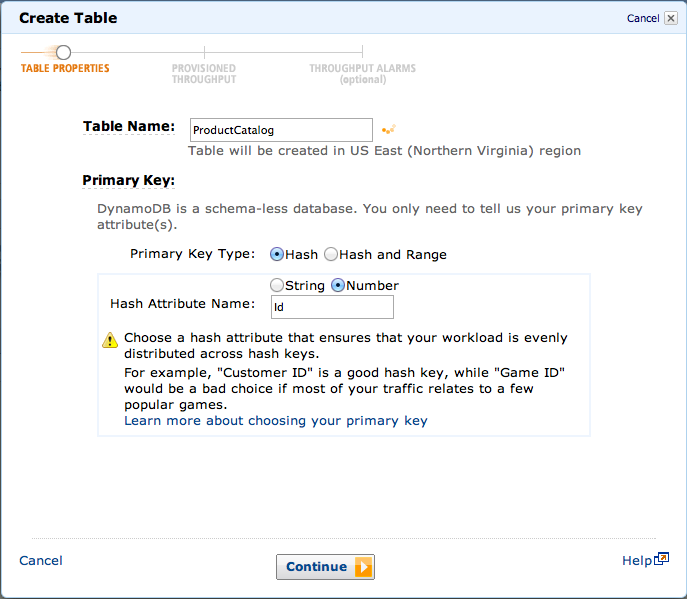
Management ConsoleでProductCatalogテーブルを作成する
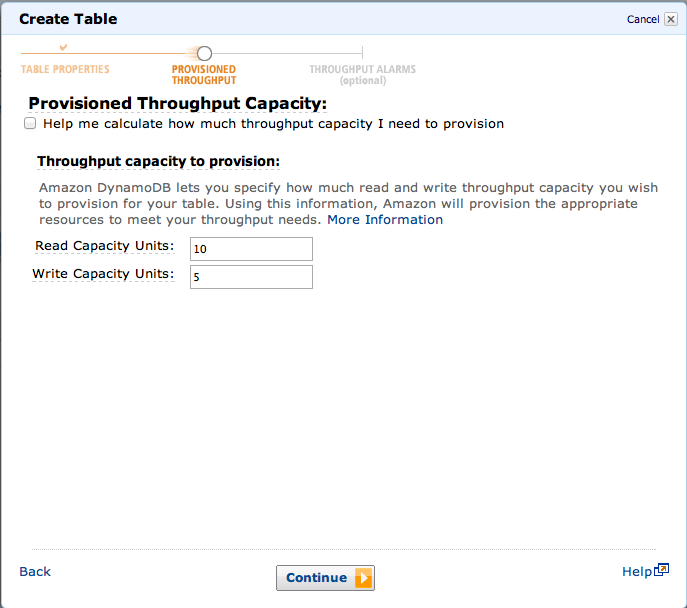
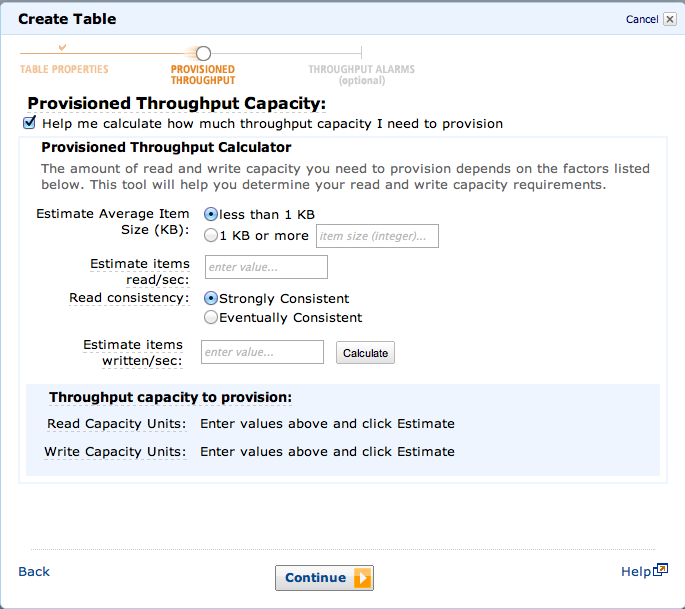
次にスループットを指定します。
HELPを見ながら計算することもできます。
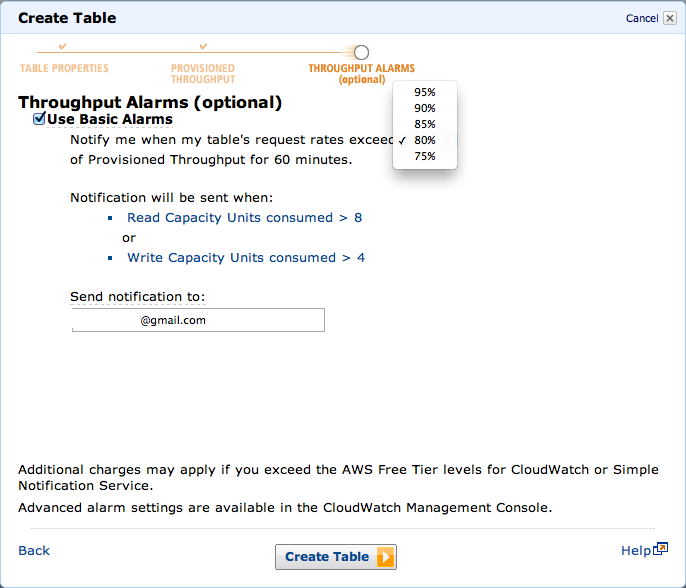
CloudWatchのアラートを設定することもできます。
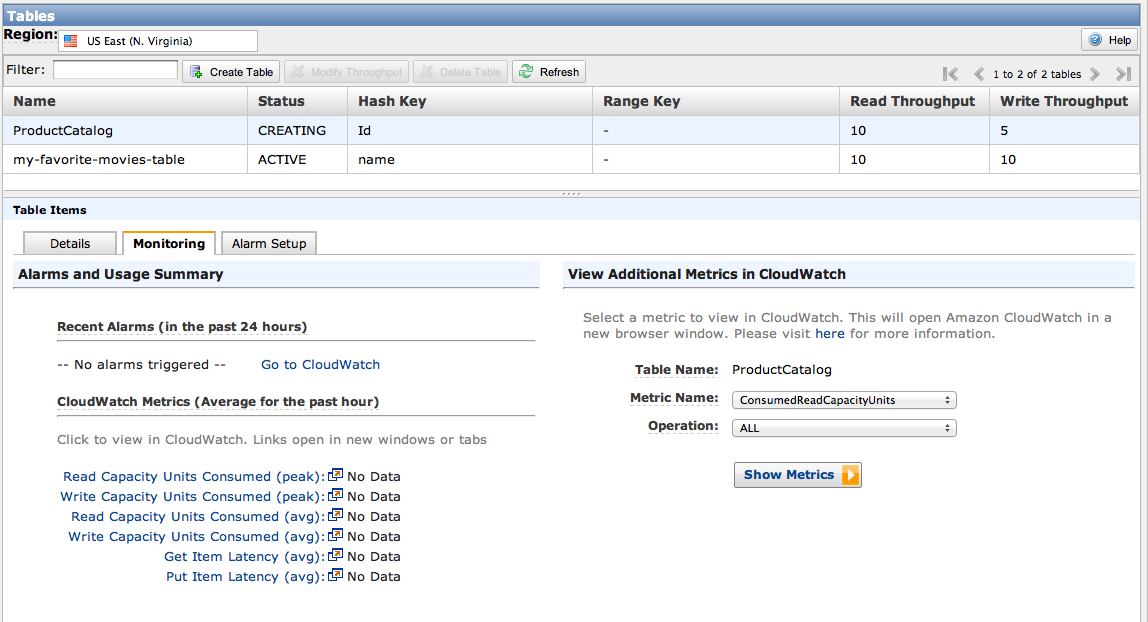
作成が完了すると一覧に表示されます。
JavaからProductCatalogテーブルへアイテムをアップロードする
ソースはこんな感じです
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import com.amazonaws.AmazonServiceException;
import com.amazonaws.auth.AWSCredentials;
import com.amazonaws.auth.PropertiesCredentials;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodb.AmazonDynamoDBClient;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodb.model.AttributeValue;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodb.model.PutItemRequest;
public class AmazonDynamoDBProductCatalogUpload {
static AmazonDynamoDBClient client;
static SimpleDateFormat dateFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z'");
static String productCatalogTableName = "ProductCatalog";
static String forumTableName = "Forum";
static String threadTableName = "Thread";
static String replyTableName = "Reply";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
createClient();
try {
uploadSampleProducts(productCatalogTableName);
} catch (AmazonServiceException ase) {
System.err.println("Data load script failed.");
}
}
private static void createClient() throws Exception {
AWSCredentials credentials = new PropertiesCredentials(
AmazonDynamoDBProductCatalogUpload.class.getResourceAsStream("AwsCredentials.properties"));
client = new AmazonDynamoDBClient(credentials);
}
private static void uploadSampleProducts(String tableName) {
try {
// Add books.
Map<String, AttributeValue> item = new HashMap<String, AttributeValue>();
item.put("Id", new AttributeValue().withN("101"));
item.put("Title", new AttributeValue().withS("Book 101 Title"));
item.put("ISBN", new AttributeValue().withS("111-1111111111"));
item.put("Authors", new AttributeValue().withSS(Arrays.asList("Author1")));
item.put("Price", new AttributeValue().withN("2"));
item.put("Dimensions", new AttributeValue().withS("8.5 x 11.0 x 0.5"));
item.put("PageCount", new AttributeValue().withN("500"));
item.put("InPublication", new AttributeValue().withN("1"));
item.put("ProductCategory", new AttributeValue().withS("Book"));
PutItemRequest itemRequest = new PutItemRequest().withTableName(tableName).withItem(item);
client.putItem(itemRequest);
item.clear();
item.put("Id", new AttributeValue().withN("102"));
item.put("Title", new AttributeValue().withS("Book 102 Title"));
item.put("ISBN", new AttributeValue().withS("222-2222222222"));
item.put("Authors", new AttributeValue().withSS(Arrays.asList("Author1", "Author2")));
item.put("Price", new AttributeValue().withN("20"));
item.put("Dimensions", new AttributeValue().withS("8.5 x 11.0 x 0.8"));
item.put("PageCount", new AttributeValue().withN("600"));
item.put("InPublication", new AttributeValue().withN("1"));
item.put("ProductCategory", new AttributeValue().withS("Book"));
itemRequest = new PutItemRequest().withTableName(tableName).withItem(item);
client.putItem(itemRequest);
item.clear();
item.put("Id", new AttributeValue().withN("103"));
item.put("Title", new AttributeValue().withS("Book 103 Title"));
item.put("ISBN", new AttributeValue().withS("333-3333333333"));
item.put("Authors", new AttributeValue().withSS(Arrays.asList("Author1", "Author2")));
// Intentional. Later we run scan to find price error. Find items > 1000 in price.
item.put("Price", new AttributeValue().withN("2000"));
item.put("Dimensions", new AttributeValue().withS("8.5 x 11.0 x 1.5"));
item.put("PageCount", new AttributeValue().withN("600"));
item.put("InPublication", new AttributeValue().withN("0"));
item.put("ProductCategory", new AttributeValue().withS("Book"));
itemRequest = new PutItemRequest().withTableName(tableName).withItem(item);
client.putItem(itemRequest);
item.clear();
// Add bikes.
item.put("Id", new AttributeValue().withN("201"));
item.put("Title", new AttributeValue().withS("18-Bike-201")); // Size, followed by some title.
item.put("Description", new AttributeValue().withS("201 Description"));
item.put("BicycleType", new AttributeValue().withS("Road"));
item.put("Brand", new AttributeValue().withS("Mountain A")); // Trek, Specialized.
item.put("Price", new AttributeValue().withN("100"));
item.put("Gender", new AttributeValue().withS("M")); // Men's
item.put("Color", new AttributeValue().withSS(Arrays.asList("Red", "Black")));
item.put("ProductCategory", new AttributeValue().withS("Bicycle"));
itemRequest = new PutItemRequest().withTableName(tableName).withItem(item);
client.putItem(itemRequest);
item.clear();
item.put("Id", new AttributeValue().withN("202"));
item.put("Title", new AttributeValue().withS("21-Bike-202"));
item.put("Description", new AttributeValue().withS("202 Description"));
item.put("BicycleType", new AttributeValue().withS("Road"));
item.put("Brand", new AttributeValue().withS("Brand-Company A"));
item.put("Price", new AttributeValue().withN("200"));
item.put("Gender", new AttributeValue().withS("M"));
item.put("Color", new AttributeValue().withSS(Arrays.asList("Green", "Black")));
item.put("ProductCategory", new AttributeValue().withS("Bicycle"));
itemRequest = new PutItemRequest().withTableName(tableName).withItem(item);
client.putItem(itemRequest);
item.clear();
item.put("Id", new AttributeValue().withN("203"));
item.put("Title", new AttributeValue().withS("19-Bike-203"));
item.put("Description", new AttributeValue().withS("203 Description"));
item.put("BicycleType", new AttributeValue().withS("Road"));
item.put("Brand", new AttributeValue().withS("Brand-Company B"));
item.put("Price", new AttributeValue().withN("300"));
item.put("Gender", new AttributeValue().withS("W")); // Women's
item.put("Color", new AttributeValue().withSS(Arrays.asList("Red", "Green", "Black")));
item.put("ProductCategory", new AttributeValue().withS("Bicycle"));
itemRequest = new PutItemRequest().withTableName(tableName).withItem(item);
client.putItem(itemRequest);
item.clear();
item.put("Id", new AttributeValue().withN("204"));
item.put("Title", new AttributeValue().withS("18-Bike-204"));
item.put("Description", new AttributeValue().withS("204 Description"));
item.put("BicycleType", new AttributeValue().withS("Mountain"));
item.put("Brand", new AttributeValue().withS("Brand-Company B"));
item.put("Price", new AttributeValue().withN("400"));
item.put("Gender", new AttributeValue().withS("W"));
item.put("Color", new AttributeValue().withSS(Arrays.asList("Red")));
item.put("ProductCategory", new AttributeValue().withS("Bicycle"));
itemRequest = new PutItemRequest().withTableName(tableName).withItem(item);
client.putItem(itemRequest);
item.clear();
item.put("Id", new AttributeValue().withN("205"));
item.put("Title", new AttributeValue().withS("20-Bike-205"));
item.put("Description", new AttributeValue().withS("205 Description"));
item.put("BicycleType", new AttributeValue().withS("Hybrid"));
item.put("Brand", new AttributeValue().withS("Brand-Company C"));
item.put("Price", new AttributeValue().withN("500"));
item.put("Gender", new AttributeValue().withS("B")); // Boy's
item.put("Color", new AttributeValue().withSS(Arrays.asList("Red", "Black")));
item.put("ProductCategory", new AttributeValue().withS("Bicycle"));
itemRequest = new PutItemRequest().withTableName(tableName).withItem(item);
client.putItem(itemRequest);
} catch (AmazonServiceException ase) {
System.err.println("Failed to create item in " + tableName);
}
}
}
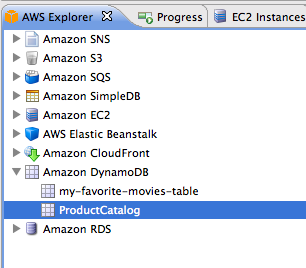
EclipseのAWS Explorerからデータを確認する
リージョンをVirginiaに変更してから確認します。ちゃんとDynamoDBが追加されていますね!
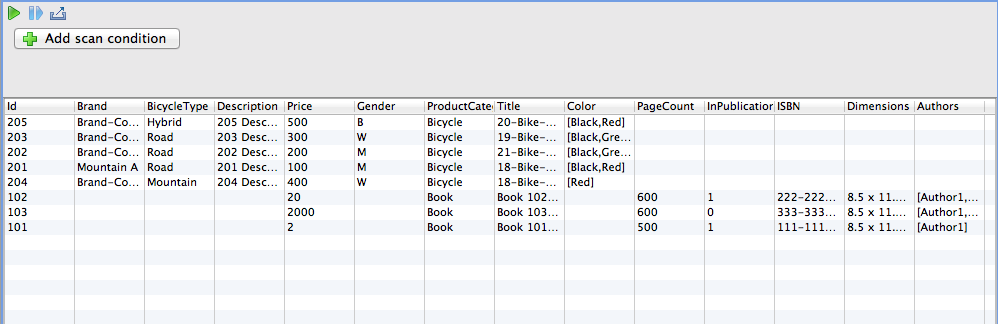
ProductCatalogテーブルのアイテム一覧を表示します
まとめ
今回は、Amazon DynamoDBのリリース直後ということで、まずは特徴を掴んでサンプルを実行してみました。指定したパフォーマンスでデータを挿入や取得できるというのが最大のポイントですね!ソーシャルゲームにはピッタリのプラットフォームかと思います。Amazon DynamoDBをマスターして、パフォーマンス王になろう!